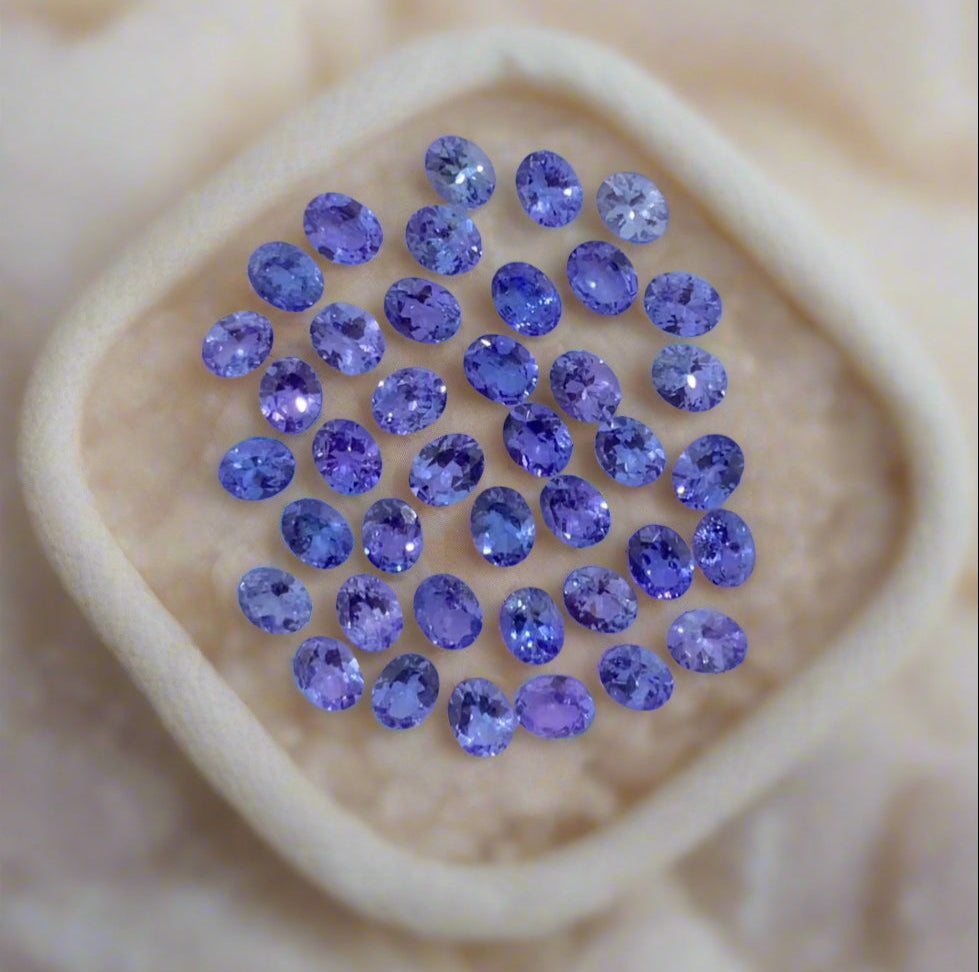
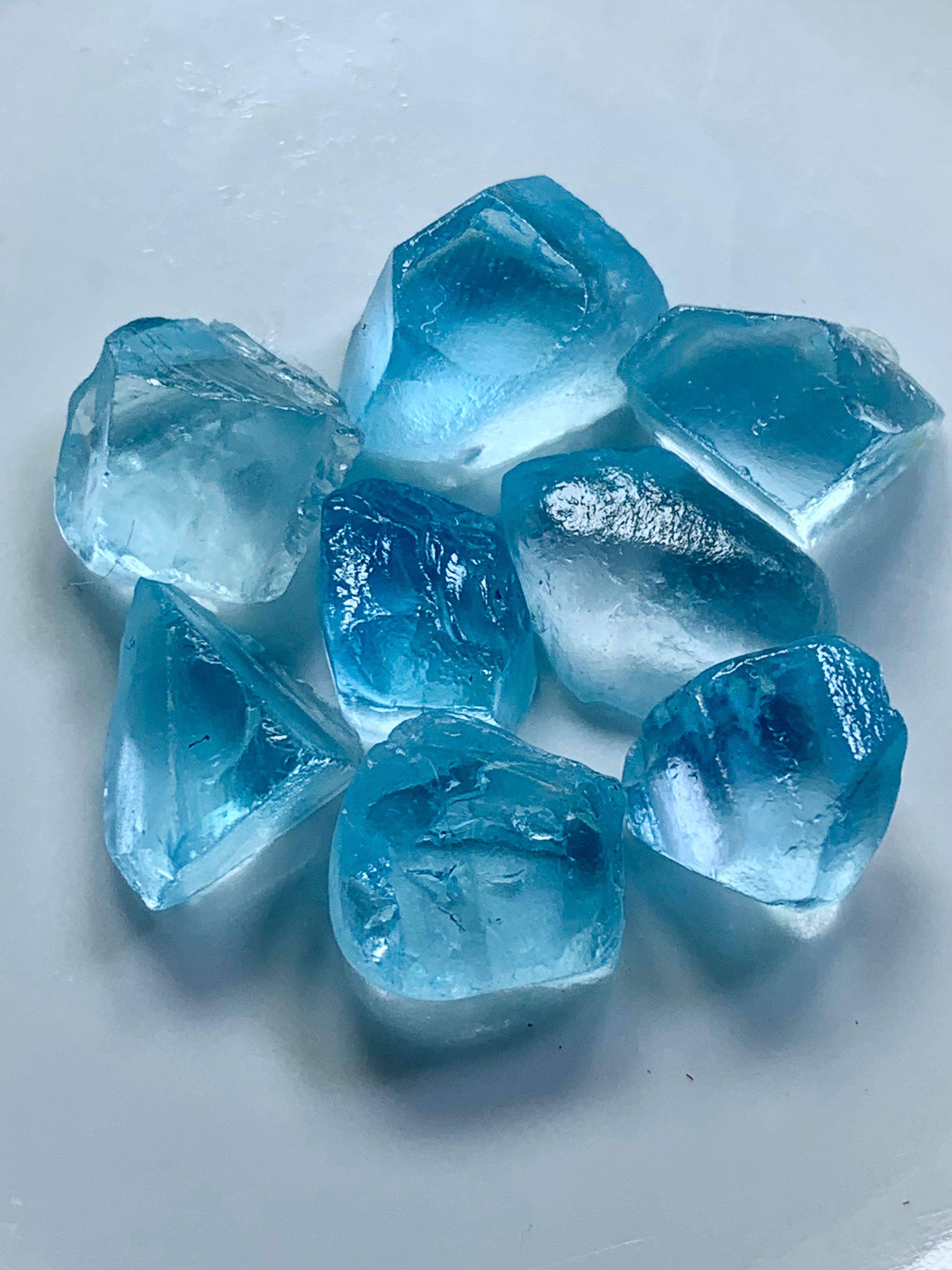
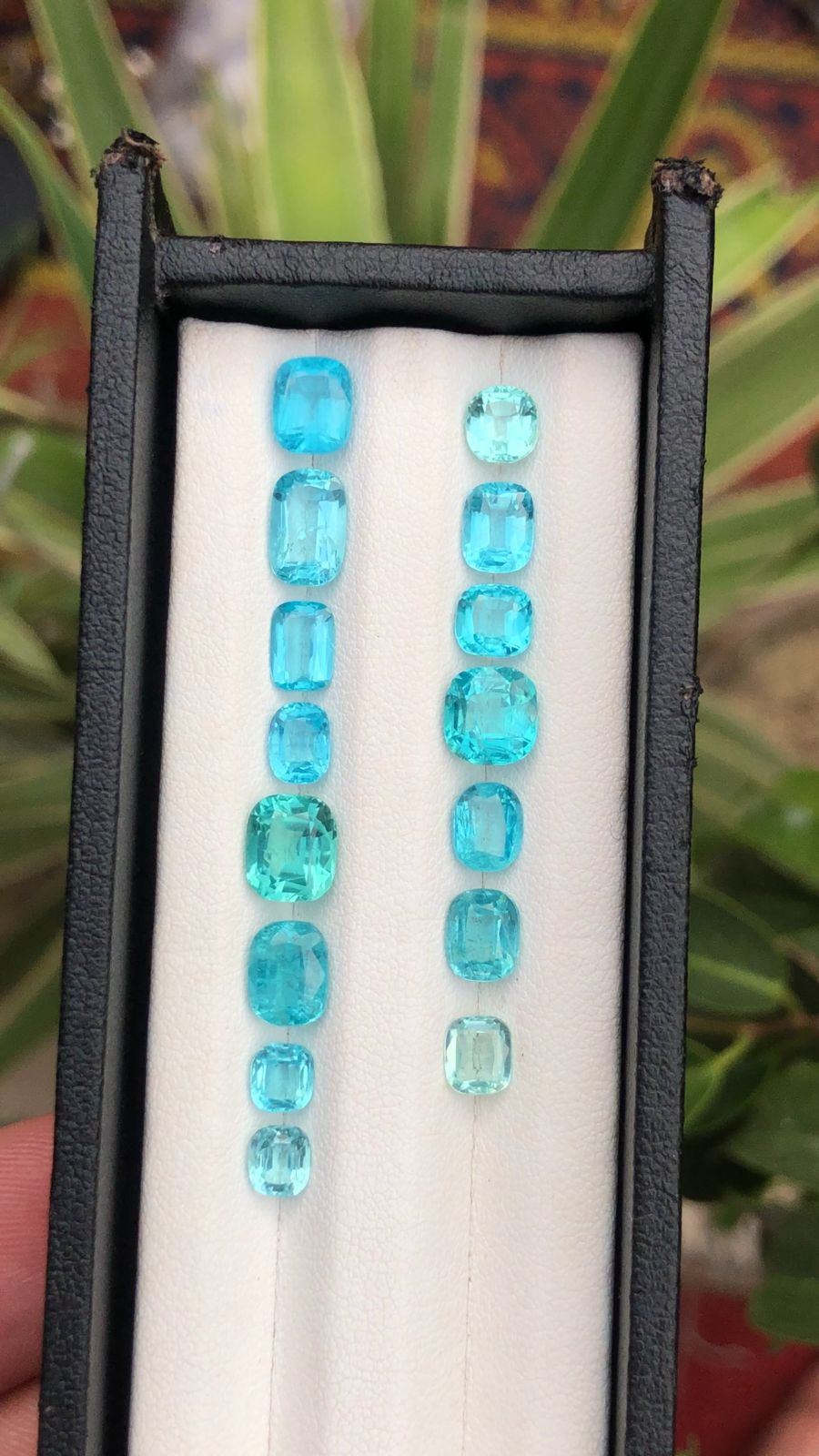
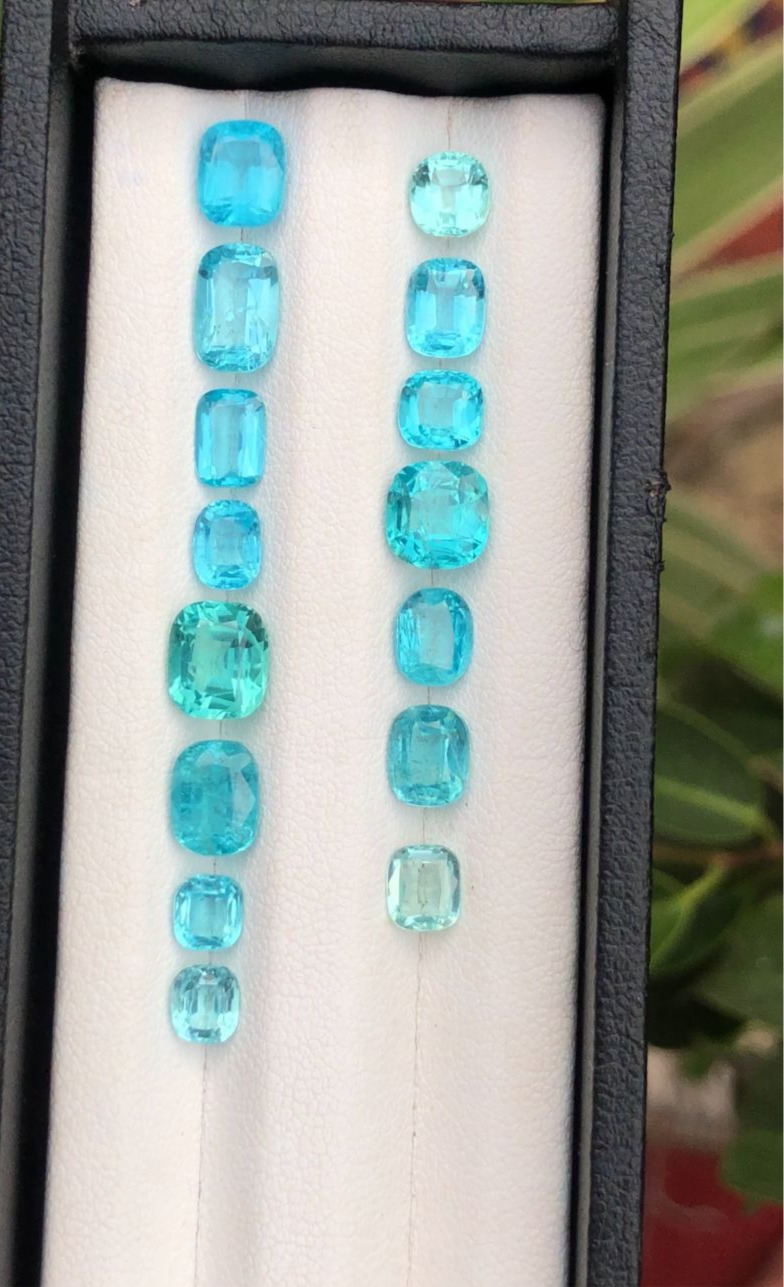
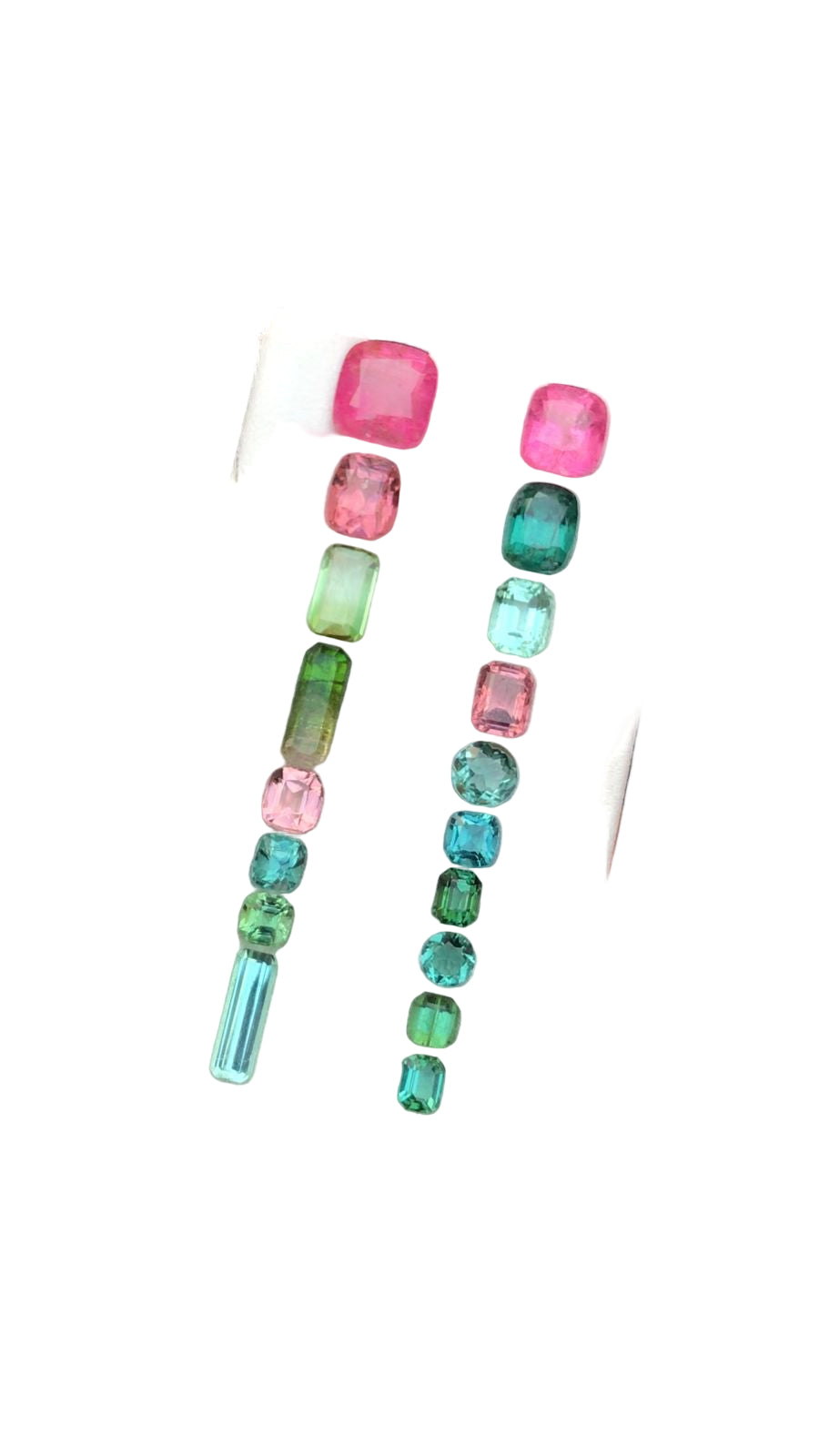
Here, we take pride to share with you comprehensive researches, providing valuable insights and information about natural gemstones and minerals. Our content covers a wide array of topics, including:-
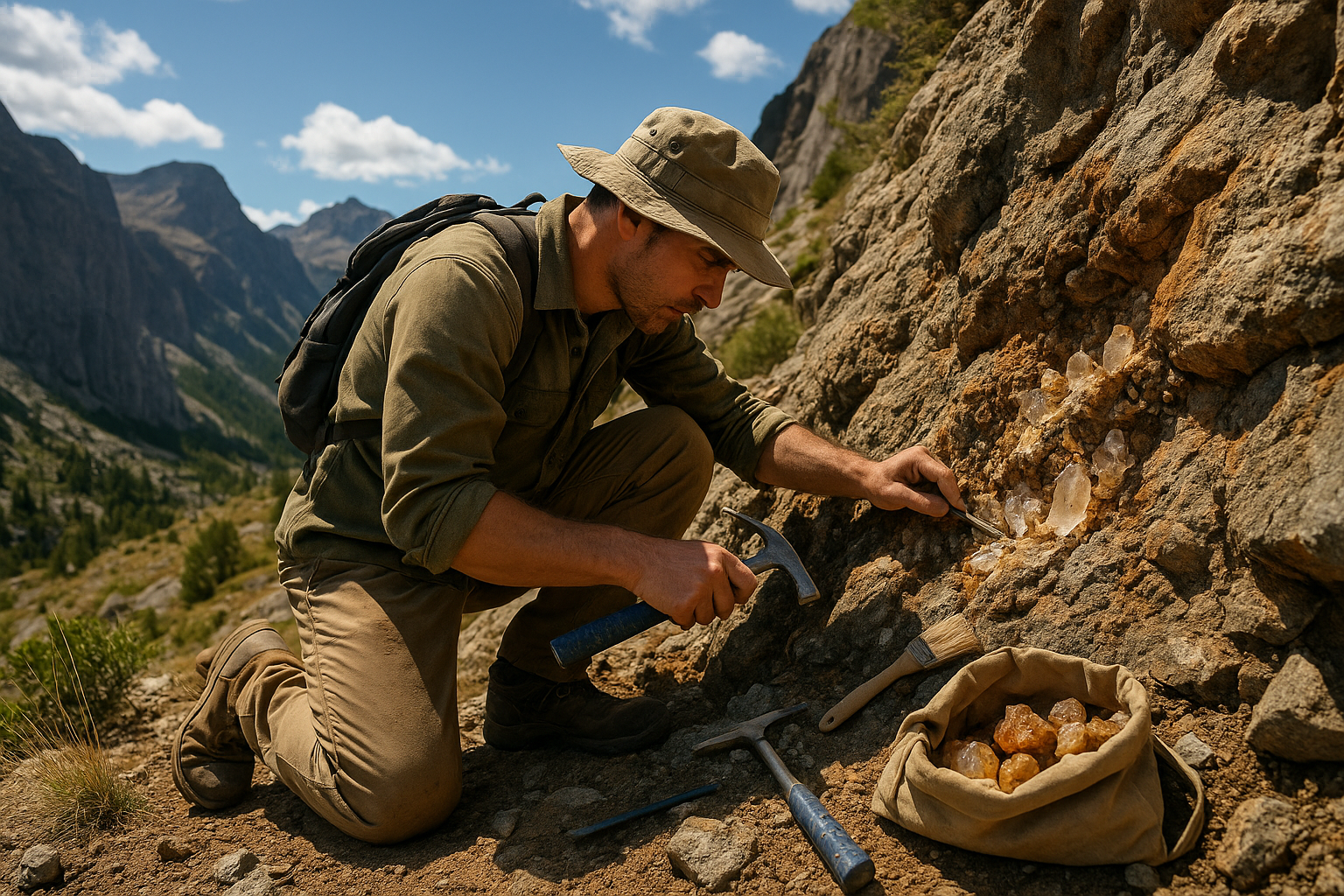
- Research Works on Gems and Minerals: Stay updated with the latest scientific research and discoveries in the field of gemology and mineralogy. We explore cutting-edge studies , plan exploration plans, gemstone hunting activities to share insights into the characteristics and properties of various gemstones and minerals.
- Geology and Mineralogy of Gemstones: Explore the geological processes behind the formation of gemstones. Learn about the environments, conditions, and geological events that contribute to the creation of these precious natural wonders. We have highlighted the details of mineralogy, understanding the composition and structure of different types of gemstones and minerals. Explore the unique properties that make each stone distinct and valuable.
- healing crystals
- Gemstones and Crystal Shopping
- Faceting and Lapidary Tips and Techniques
- Birthstones
- Information about Precious-stones and semi-precious stones list
- Gemstone Jewelry Designing Tips
- Exploring Geography and Gemstone Mining: Discover the geographical locations around the globe where gemstones are mined. From the depths of mines to the surface of the earth, we explore the journey of gemstones from their origins to their extraction.
- New Findings in Gemstones: Learn about the latest discoveries s in the gemstone realm. Our blog keeps you updated on new gemstone deposits, rare earth minerals finds, and emerging trends in the gemstone industry.
- Crystal Structure and Formation: Gain insights into the e crystal structures and formation processes of gemstones and minerals. Explore the science behind their unique shapes, colors, and properties.
- Scientific Facts and Insights: Delight in learning fascinating scientific facts and insights about gemstones and minerals. From their historical significance to their cultural symbolism, we cover a diverse range of topics related to these natural marvels.
Whether you're a student of gemologist, a curious gemstone enthusiast, or simply someone with a passion for natural beauty and science, our blog aims to provide valuable resources and engaging content to deepen your understanding and appreciation of gemstones and minerals. Join us on this exciting journey of discovery!
Blog - Learn Natural Gemstones, Minerals, Crystals Info, News, Tips, Researches
The Top Gemstone Jewelry Trends 2025
Are There Any Gemstones That Have Applications in the Scientific Community
How to Choose the Perfect Polished Gemstone for Jewelry?
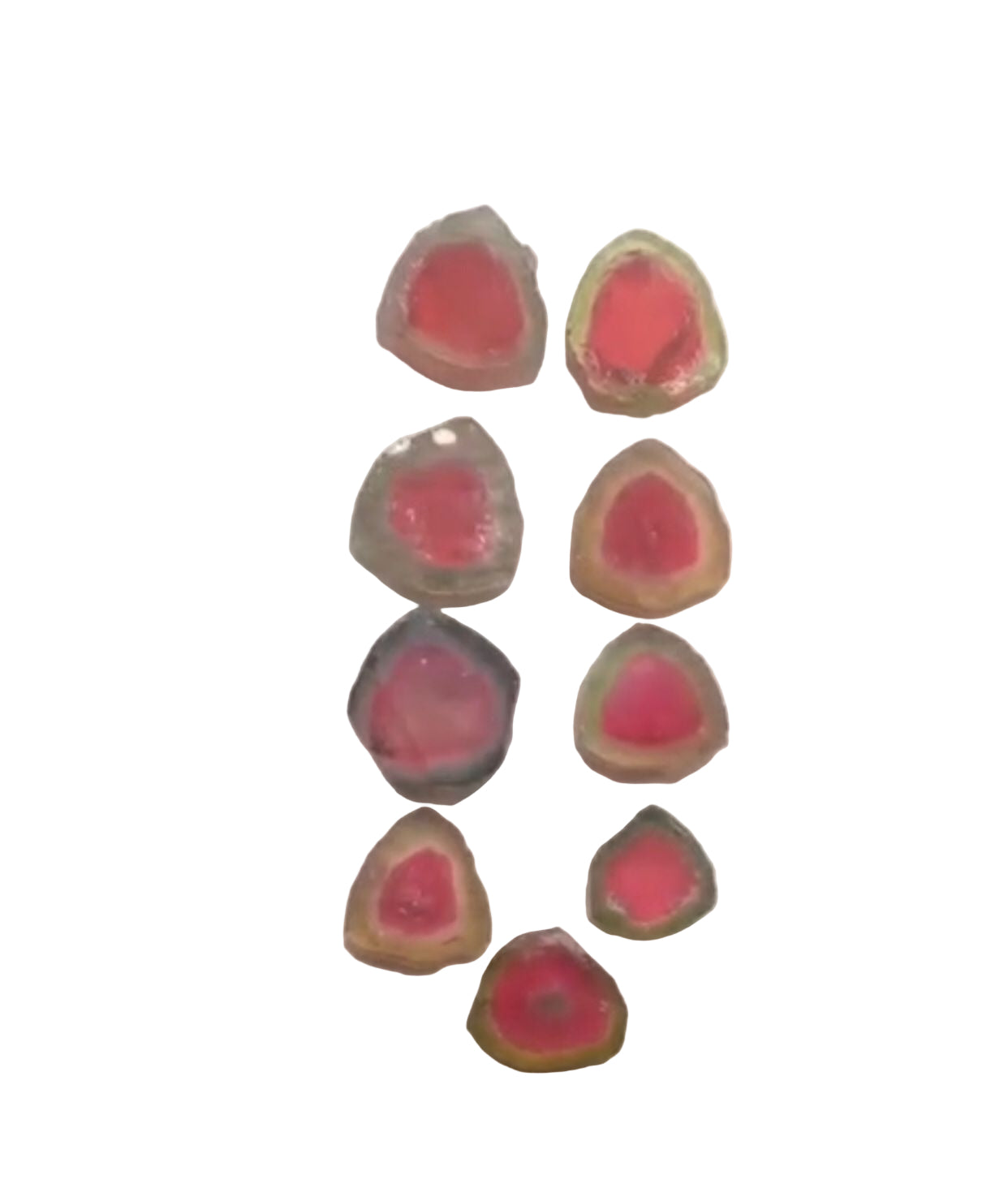
How do I know if My Garnet Gemstone is Valuable?
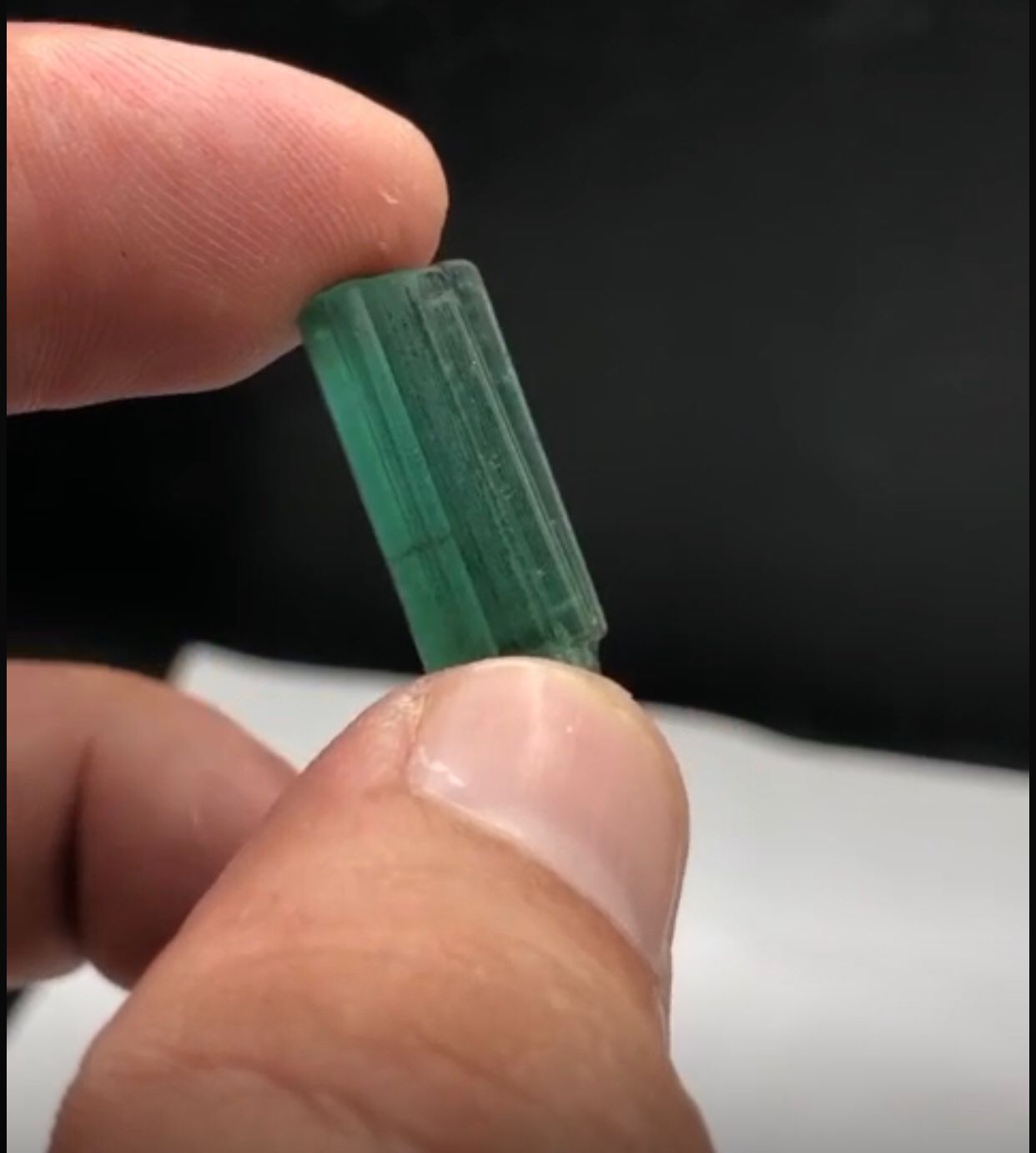
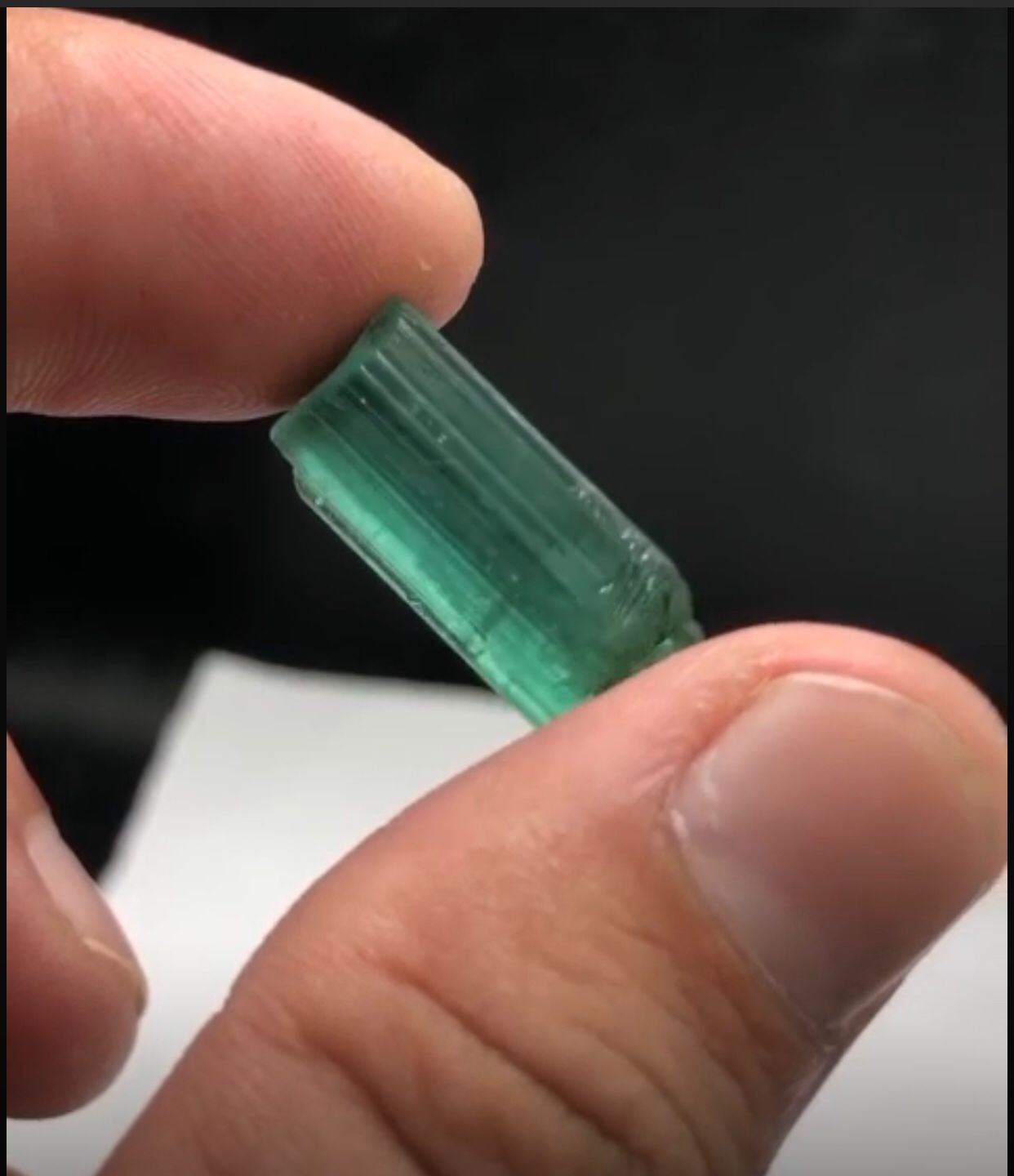
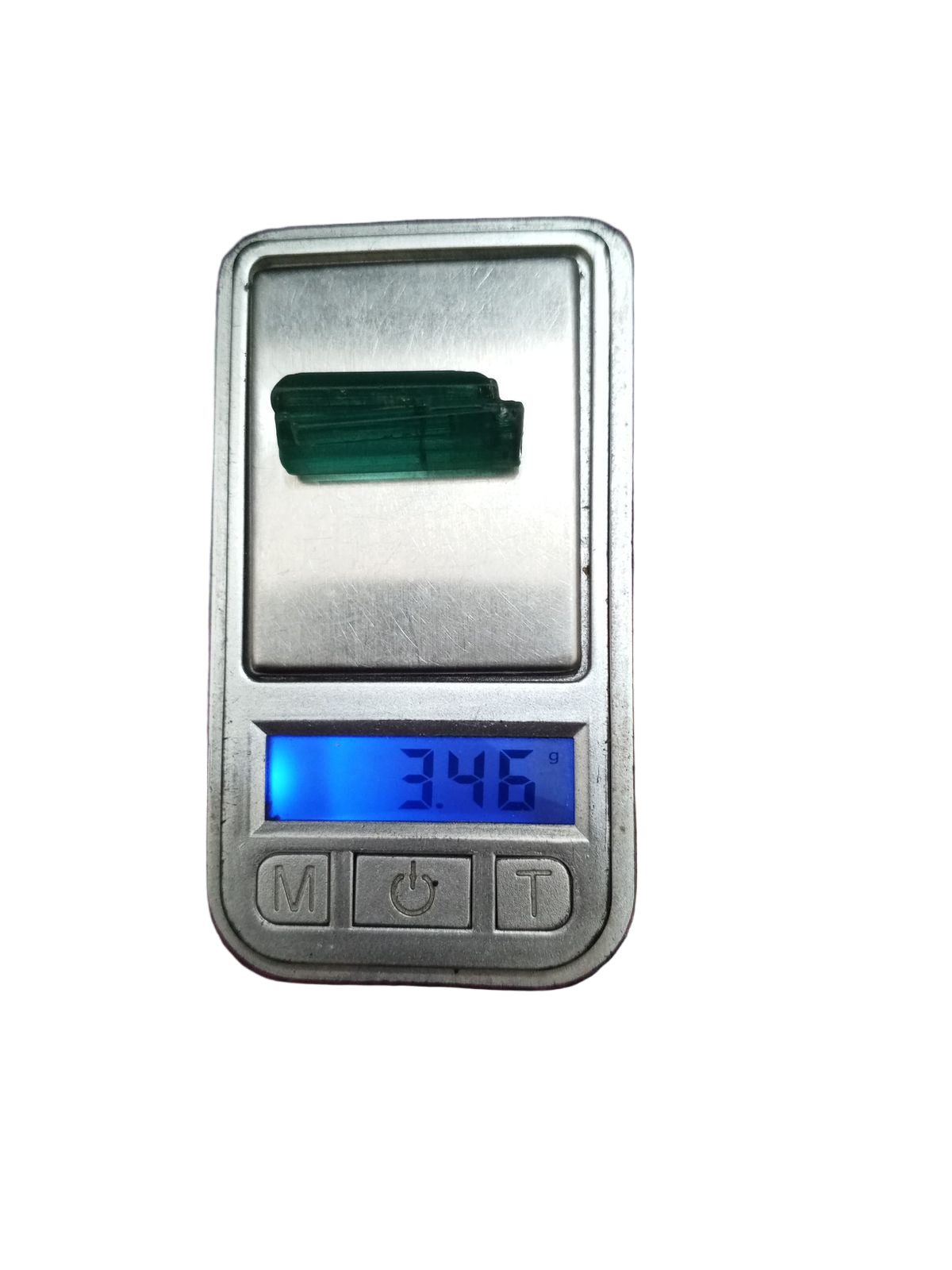
About Natural Panjsheir Emeralds from Afghanistan
Gemstones of the Ancient World; Uncovering the Treasured Gemstones of the Antiquated Civilization
Common FAQs About Buying Loose Gemstones
Faceting for Beginners: Transform Uncut Gemstones into Masterpiece
Is Zircon a Birthstone of December?
From Rockhound to Seller: Richard's Journey to Identifying and Selling Gemstones
Shocking Secrets of Natural Crystals: What Nikola Tesla Discovered
Is It Safe to Buy Gemstones Online? The Story of Alex and the Emily